Transform your traditional house into a zero energy home by combining advanced energy-efficient home design with renewable power generation. These innovative dwellings produce as much clean energy as they consume annually, slashing utility bills to zero while fighting climate change.
Zero energy homes represent the future of sustainable living, combining superior insulation, airtight construction, and high-performance windows with rooftop solar panels and smart energy management systems. While the initial investment typically runs 5-15% higher than traditional construction, homeowners recover costs through eliminated energy bills, increased property values, and available tax incentives.
Whether building new or retrofitting an existing home, achieving zero energy status starts with maximizing efficiency through proper orientation, thermal barriers, and strategic window placement. Advanced mechanical systems like heat pumps and energy recovery ventilators then minimize remaining energy needs before solar panels generate clean electricity to offset consumption.
The shift toward zero energy homes continues gaining momentum as more homeowners recognize both the environmental benefits and compelling financial returns. With energy costs rising and climate concerns mounting, these self-sustaining dwellings offer a practical path to eliminate utility bills while ensuring a more sustainable future.
What Makes a Home Truly Zero Energy?
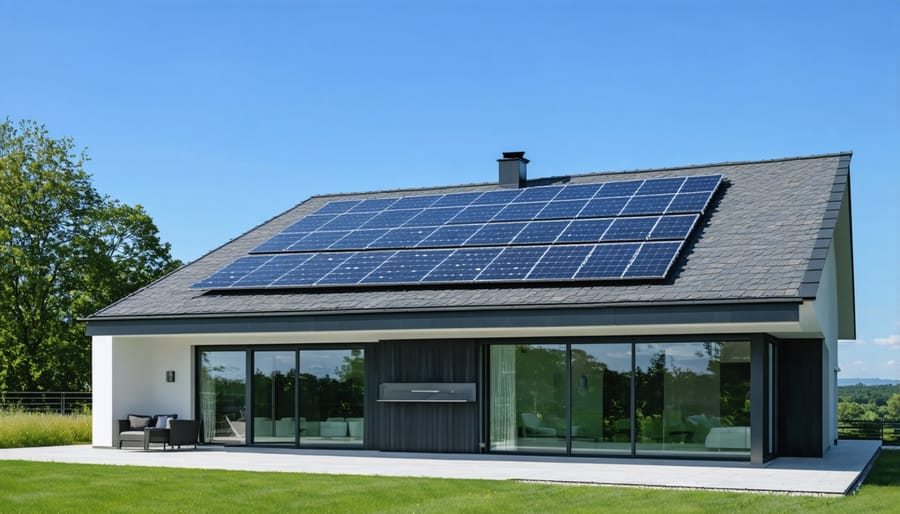

Energy Production vs. Consumption
A zero energy home works by striking a perfect balance between the energy it produces and consumes over a year. Think of it like maintaining a balanced checkbook – your home generates enough renewable energy to offset what it uses for daily living.
Most zero energy homes rely on solar panels to generate electricity, typically producing excess power during sunny days. This surplus energy goes back to the power grid, acting like a credit system. When the sun isn’t shining or during high-usage periods, the home draws power from the grid, using those credits.
The key to success lies in minimizing energy consumption first. This means investing in superior insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and smart home systems that optimize energy use. LED lighting, programmable thermostats, and Energy Star certified equipment all play crucial roles in reducing the home’s energy appetite.
To achieve true zero energy status, your home’s annual energy production must match or exceed its consumption. This balance is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and typically requires careful planning and monitoring throughout the year.
Key Components of Zero Energy Design
Creating a zero energy home requires several key components working together seamlessly. At the heart of these homes is superior insulation and air sealing, which form the foundation of energy efficiency. Think of your home as a thermos – the better insulated it is, the less energy you’ll need to maintain comfortable temperatures.
High-performance windows and doors play a crucial role too. Double or triple-pane windows with low-E coatings and proper weatherstripping help maintain indoor temperatures while letting in natural light and heat when desired.
The heating and cooling system is another vital component. Energy-efficient heat pumps have become the go-to choice, as they can both heat and cool your home using minimal electricity. These are often paired with energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) that maintain fresh air while preserving indoor temperature.
Solar panels are typically the star of the show, generating clean electricity to power your home. They’re usually accompanied by smart energy monitoring systems that help you track and optimize your energy usage.
Energy-efficient appliances and LED lighting round out the package, ensuring that every watt of electricity is used wisely. Water-saving fixtures and smart home technologies can further reduce your home’s overall energy needs.
Remember, these components work best when they’re part of a whole-house approach, where each element complements the others to achieve true zero energy status.
Smart Design Features for Maximum Efficiency
Passive Solar Design
Harnessing the sun’s natural power through smart home design is one of the most effective ways to achieve zero energy living. The key lies in strategic home orientation and thoughtful window placement, working together with other energy-saving lighting strategies to maximize efficiency.
In the Northern Hemisphere, positioning your home’s longest walls to face south allows for maximum sun exposure during winter months when the sun sits lower in the sky. Large, south-facing windows capture valuable heat during cold seasons, while shorter east and west walls minimize unwanted heat gain during summer mornings and afternoons.
Strategic window placement isn’t just about heating – it’s about creating a natural flow of air throughout your home. Placing windows on opposite walls encourages cross-ventilation, reducing the need for artificial cooling. Adding roof overhangs or awnings above south-facing windows provides shade during summer while still allowing winter sun to warm your home.
Consider incorporating thermal mass materials like concrete floors or stone walls near these windows. These materials absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, helping maintain comfortable temperatures naturally. For existing homes, you can optimize passive solar benefits by adding window films, thermal curtains, or strategically placed trees for seasonal shade.
Remember, successful passive solar design is about finding the right balance between heat gain and loss throughout the year, working with your local climate rather than against it.

Insulation and Air Sealing
Proper insulation and air sealing are the foundation of any zero energy home, acting like a cozy blanket that keeps your living space comfortable year-round. Today’s eco-friendly insulation solutions go far beyond traditional fiberglass, offering superior performance while being kind to the environment.
The key to maximum efficiency lies in creating an unbroken thermal envelope around your home. This starts with high-performance insulation in walls, floors, and ceilings, typically achieving R-values that exceed standard building codes by 25-50%. Modern options include blown-in cellulose, spray foam, and structural insulated panels (SIPs), each offering unique benefits for different applications.
But insulation is only half the story. Air sealing is equally crucial, as even tiny gaps can lead to significant energy losses. Focus on sealing common trouble spots like window frames, door jambs, electrical outlets, and where utilities enter your home. Advanced techniques like blower door testing help identify hidden air leaks that might otherwise go unnoticed.
For best results, combine multiple approaches: use spray foam around windows and doors, weatherstripping for moving parts, and caulk for smaller gaps. Don’t forget about often-overlooked areas like attic hatches and basement rim joists. These comprehensive insulation and air sealing strategies can reduce your home’s energy needs by up to 50%, making that zero energy goal much more achievable.
Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
Windows and doors play a crucial role in achieving zero energy status, acting as your home’s thermal envelope gatekeepers. High-performance windows with double or triple panes filled with insulating gas (typically argon or krypton) can dramatically reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
When selecting windows, look for those with a low U-factor (ideally below 0.30) and an appropriate Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) for your climate. In colder regions, a higher SHGC helps capture beneficial solar heat, while lower SHGC values work better in warmer climates to prevent overheating.
Energy-efficient doors should feature robust insulation cores and tight weatherstripping. Steel and fiberglass doors typically offer better thermal performance than traditional wooden ones. Pay special attention to glass elements in doors – choose models with double-pane, low-E glass to maintain efficiency.
Installation is just as important as the products themselves. Even the most efficient windows and doors won’t perform well if they’re improperly installed. Ensure proper sealing around frames and use high-quality weatherstripping to prevent air leakage. Consider professional installation for best results.
These upgrades might seem costly initially, but they typically pay for themselves through reduced energy bills within 5-10 years. Plus, they add value to your home while improving comfort by eliminating drafts and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures year-round.
Renewable Energy Systems
Solar Panel Systems
Solar panel systems are the heartbeat of any zero energy home, converting abundant sunlight into clean, usable electricity. The two main types you’ll encounter are grid-tied systems, which connect to the local power grid, and off-grid systems that work independently with battery storage.
For most homeowners, grid-tied systems offer the perfect balance of reliability and cost-effectiveness. These systems generate electricity during sunny days and send excess power back to the grid, essentially making your meter run backward. When the sun isn’t shining, you’ll draw power from the grid as needed.
A typical residential solar system consists of panels (usually mounted on the roof), an inverter to convert DC power to AC, and monitoring equipment to track performance. The number of panels you’ll need depends on your home’s energy consumption and available roof space – most homes require between 20-24 panels for complete energy coverage.
Installation is best handled by certified professionals, though many homeowners choose to participate in the planning process. They’ll assess your roof’s orientation, angle, and structural integrity before designing a system that maximizes sun exposure. South-facing roofs typically yield the best results, but east and west exposures can also work well.
The benefits extend beyond environmental impact. Modern solar panels can last 25-30 years, significantly increasing your home’s value while eliminating or drastically reducing your electricity bills. Many regions offer tax incentives and rebates, making the initial investment more manageable.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage is the key to making your zero energy home truly self-sufficient. The most popular option is a home battery system, similar to the Tesla Powerwall or LG Chem RESU, which stores excess solar energy generated during sunny days for use at night or during cloudy weather.
Think of these batteries as your home’s personal energy bank account – you deposit power when the sun is shining and withdraw it when needed. Most modern systems are compact wall-mounted units that can be installed in your garage or utility room, taking up minimal space while providing maximum benefit.
What makes these systems even smarter is their integration with energy management technologies. Smart controllers automatically decide when to store power and when to use it, helping you maximize savings. During peak rate hours, your home can run on stored energy instead of drawing expensive power from the grid. These systems can even learn your household’s energy patterns to optimize usage further.
For backup power during outages, many homeowners pair their battery systems with generators. While this adds to the initial investment, it provides complete peace of mind and energy independence. The best part? Many energy storage solutions now come with user-friendly apps that let you monitor and control your home’s energy flow right from your smartphone.
Remember, while battery systems represent a significant upfront cost, they’re essential for achieving true zero energy status and can pay for themselves through reduced utility bills and energy independence.

Cost Considerations and ROI
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
While the upfront costs of a zero energy home can seem daunting, the long-term financial benefits often make it a smart investment. On average, converting a standard home to zero energy status costs between $30,000 and $60,000 above traditional construction costs. However, these figures can vary significantly based on your location, home size, and existing infrastructure.
The good news? Homeowners typically recoup their investment within 7-10 years through dramatic reductions in utility bills. A zero energy home can help you maximize energy savings by eliminating monthly energy costs entirely, potentially saving $2,000-$4,000 annually depending on your local utility rates.
Consider this breakdown: While a solar panel system might cost $20,000, it can generate $1,800 in annual savings. High-efficiency HVAC systems and premium insulation might add $15,000 but reduce heating and cooling costs by 50-70%. Energy-efficient windows and doors, though pricier initially, can save hundreds each year in temperature control.
Many homeowners also benefit from available tax incentives, rebates, and increased property values. Studies show that zero energy homes typically sell for 5-10% more than traditional homes, adding another layer of financial benefit to your investment.
Available Incentives and Rebates
Making the switch to a zero energy home is more affordable than ever, thanks to numerous government incentives and rebates available across the country. The federal government offers a substantial 30% tax credit through the Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Credit for qualifying energy-efficient upgrades, including solar panels, heat pumps, and improved insulation.
Many states sweeten the deal with additional incentives. For example, California’s PACE (Property Assessed Clean Energy) program helps homeowners finance energy improvements through property tax assessments, while New York offers generous grants through their NY-Sun initiative for solar installations.
Local utility companies often provide rebates for energy-efficient appliances and smart home technologies. Some even offer reduced electricity rates for homes with solar panels or other renewable energy systems.
Don’t overlook manufacturer rebates either. Many companies producing energy-efficient appliances, windows, and HVAC systems offer cash back or special financing options to encourage sustainable choices.
To maximize your savings, consider combining multiple incentives. For instance, you could pair federal tax credits with state rebates and utility company incentives for the same project. Visit the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) website to find available programs in your area, and remember to consult with a tax professional about eligibility requirements and documentation needed for tax credits.
Steps to Transform Your Home
Energy Audit and Assessment
Before diving into zero energy renovations, it’s essential to understand your home’s current energy performance. Start with a thorough home energy assessment tips to identify where you’re losing energy and money.
Begin by gathering your utility bills from the past year to establish your baseline energy consumption. Next, conduct a room-by-room inspection, checking for air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings. Pay special attention to your insulation, HVAC system, and major appliances.
Consider investing in an infrared camera inspection to detect hidden heat loss areas, or hire a professional energy auditor for a comprehensive assessment. They’ll use specialized equipment like blower doors and thermal imaging to create a detailed energy profile of your home.
Make a prioritized list of improvements based on your findings. Focus on the most significant energy drains first – typically air sealing, insulation upgrades, and HVAC improvements. This systematic approach ensures your journey toward zero energy is both efficient and cost-effective.
Remember to document everything thoroughly, as this information will help track your progress and validate improvements over time.
Phased Implementation Plan
Transforming your home into a zero energy dwelling doesn’t have to happen overnight. A smart, phased approach can make the transition more manageable and budget-friendly. Start with the basics: conduct a home energy audit and tackle simple improvements like sealing air leaks and adding insulation. These low-cost updates create a solid foundation for future upgrades.
Next, focus on upgrading your appliances and lighting to energy-efficient models as your existing ones reach the end of their life. This natural replacement cycle helps spread costs over time. In phase three, consider bigger investments like high-performance windows and doors, which significantly reduce energy loss.
The fourth phase typically involves installing renewable energy systems. Start with a smaller solar array that you can expand later, or begin with solar water heating before moving to full photovoltaic panels. Remember to take advantage of tax incentives and rebates at each stage – they can make premium upgrades more affordable.
Monitor your progress between phases using energy tracking tools, and adjust your timeline based on your budget and energy-saving results. This flexible approach lets you work toward your zero energy goals while maintaining financial comfort.
Embracing zero energy living isn’t just about creating a more sustainable future – it’s about taking control of your home’s energy destiny while enjoying significant long-term savings. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, achieving a zero energy home is both achievable and rewarding, whether you’re building from scratch or transforming your existing space.
Remember that every step toward energy independence counts. Start with the basics: improve your insulation, upgrade to energy-efficient appliances, and consider smart home technology to monitor and optimize your energy usage. These foundational changes create the perfect launching pad for bigger improvements like solar panels and advanced HVAC systems.
While the initial investment might seem daunting, the financial benefits of zero energy homes are undeniable. Between utility savings, increased property value, and available tax incentives, your investment typically pays for itself within 5-10 years. Plus, you’ll be joining a growing community of homeowners who are leading the charge toward a more sustainable future.
Ready to begin your zero energy journey? Start by conducting an energy audit of your home to identify your biggest opportunities for improvement. Create a realistic timeline and budget for implementing changes, and don’t hesitate to consult with energy efficiency experts who can guide you through the process.
The path to zero energy living is yours to choose – whether you take small steps or make bold changes, every energy-saving measure brings you closer to your goal. Your actions today will create a more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable home for tomorrow. Let’s make zero energy living the new standard for homes everywhere.
